When dealing with thumb and wrist pain, finding effective ways to manage discomfort and promote healing is crucial. Orthotic devices offer a non-invasive and supportive approach to alleviate pain, reduce strain, and aid in the recovery process. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of orthotic fabrication for thumb and wrist pain, highlighting how these devices can provide much-needed relief.
Understanding Orthotic Devices:
Orthotic devices are custom-made or prefabricated tools designed to support and stabilize various parts of the body. In the context of thumb and wrist pain, orthotics can help by providing proper alignment, immobilization, and protection to the affected areas. They are typically recommended by healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic specialists or physical therapists, after a thorough evaluation of the individual's condition.
Benefits of Orthotic Fabrication:
1. Pain Relief: Orthotics are designed to reduce pain by distributing pressure evenly and limiting the movement that exacerbates discomfort. By stabilizing the thumb and wrist, these devices can ease strain on inflamed or injured tissues.
2. Immobilization: For conditions like De Quervain's tenosynovitis or wrist sprains, immobilization is often necessary for healing. Orthotic devices can effectively restrict motion, allowing damaged tissues to recover without further irritation.
3. Alignment Correction: Improper alignment of the thumb and wrist can lead to chronic pain and exacerbate existing conditions. Orthotics can help correct alignment issues, promoting better joint function and reducing strain on surrounding muscles and tendons.
4. Protection During Activity: Engaging in everyday activities can sometimes aggravate thumb and wrist pain. Orthotic devices offer protection during movement, reducing the risk of further injury while allowing individuals to perform necessary tasks more comfortably.
5. Customized Fit: Custom-made orthotics are tailored to the individual's specific needs, ensuring a precise fit and optimal support. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of the device in addressing the root cause of the pain.
Types of Orthotic Devices for Thumb and Wrist Pain:
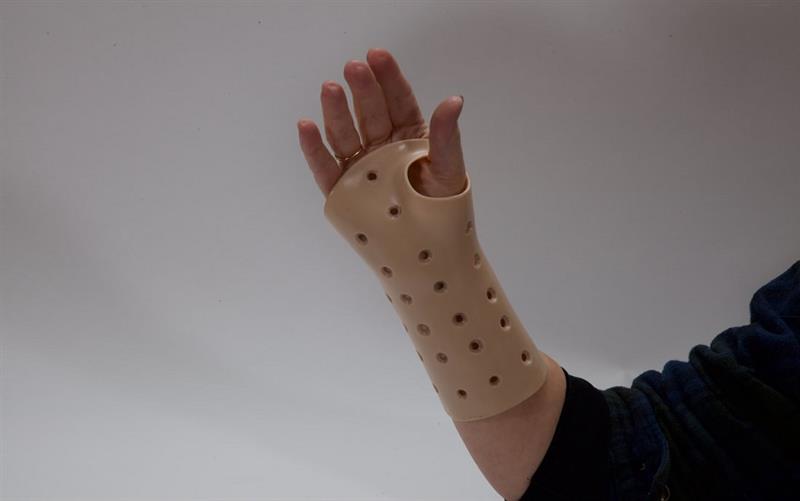
1. Wrist Splints: These devices immobilize the wrist and thumb, providing stability and reducing strain on the affected areas. They are often used for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and De Quervain's tenosynovitis.
2. Thumb Spicas: Thumb spicas offer support to the thumb while allowing movement in the fingers. They are beneficial for injuries such as thumb sprains or fractures.
3. Dynamic Orthotics: These orthotics allow controlled movement of the thumb and wrist while providing support and protection. They can be useful during rehabilitation to prevent stiffness.
4. Cock-Up Splints: These splints immobilize the wrist while allowing the fingers to move freely. They are commonly used for conditions requiring wrist stabilization.
How to diagnose Thumb and Wrist Pain?
Thumb and wrist pain can arise from a variety of underlying causes, making an accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment. From overuse injuries to inflammatory conditions, pinpointing the source of discomfort requires a thorough and systematic approach. In this article, we'll outline the steps healthcare professionals take to diagnose thumb and wrist pain, ensuring appropriate and timely intervention.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination:
The diagnostic process begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. The healthcare provider will inquire about the onset of pain, any triggering activities, and other relevant details. They will then assess the affected area for signs of inflammation, tenderness, swelling, and range of motion limitations.
2. Pain Description and Location:
Patients are often asked to describe their pain, including its intensity, quality (sharp, dull, throbbing), and whether it radiates to other areas. Identifying the exact location of pain in the thumb and wrist helps narrow down potential causes.
3. Range of Motion and Strength Assessment:
Evaluating the thumb's and wrist's range of motion and strength provides valuable insights into potential injuries or conditions affecting these areas. Limited mobility or weakness can point to specific issues.
4. Specialized Tests:
Healthcare professionals may perform specialized tests to further assess the affected structures. For instance, the Finkelstein test can help diagnose De Quervain's tenosynovitis, while the Phalen's test is used to assess carpal tunnel syndrome.
5. Imaging Studies:
Depending on the suspected diagnosis, imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be ordered. These images provide detailed views of bones, joints, tendons, and soft tissues, aiding in the identification of underlying issues.
6. Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG):
In cases where nerve-related conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome are suspected, nerve conduction studies and electromyography may be conducted to assess nerve function and detect abnormalities.
7. Blood Tests:
Blood tests can help rule out systemic conditions that may contribute to thumb and wrist pain, such as inflammatory arthritis or metabolic disorders.
Common Diagnoses for Thumb and Wrist Pain:
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis: Diagnosed through physical examination and clinical history, including the Finkelstein test.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnosed through physical examination, nerve conduction studies, and medical history.
- Wrist Sprains or Fractures: Diagnosed through physical examination and imaging studies like X-rays or MRI.
- Osteoarthritis or Inflammatory Arthritis: Diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies.
- Tendinitis: Diagnosed through physical examination, medical history, and sometimes imaging studies.